
They ensure consistency and comparability in financial management among all organizations in the United States, both for-profit and gaap for nonprofits nonprofit. Nonprofit organizations that receive revenue through public and private sources of funding use the system of fund accounting rather than traditional business methods of accounting. Fund accounting refers to the management and allocation of revenue received by nonprofits and the restrictions, or designations that are placed on those sources of revenue. In conclusion, nonprofit accounting encompasses unique principles and practices essential to manage the financial resources of an organization. Understanding these fundamentals is vital to maintaining transparency, accountability, and trust among the stakeholders they serve.
- Nonprofit organizations play a vital role in addressing social, environmental, and cultural issues, often relying on donations, grants, and funding to operate.
- By handling your nonprofit’s accounting responsibly, you’ll earn the trust of donors and foundations — and more easily accomplish your goals.
- This change should make it easier for not-for-profits to report investment activities and provide greater comparability among organizations using internal and external investment managers.
- How Development and Finance Can Get Along (Really!)Does your organization need a fund accounting system that makes it easy to adhere to GAAP reporting standards?
- Ideally, these standards should help your nonprofit maintain transparency and accountability with donors, grant funders, and the public.
Allocate Expenses by Function

The principles apply to all accounting professionals but are especially important for nonprofits because they emphasize transparency and building credibility. By handling your nonprofit’s accounting responsibly, you’ll earn the trust of donors and foundations — and more easily accomplish your goals. Understanding the key aspects of accounting will help your nonprofit better recognize the financial situation of your own organization. You should check in with your budget monthly, comparing and evaluating your budgeted revenue and gross vs net expenses against your actual revenue and expenses. In order to make the best financial decisions, nonprofit professionals should understand some accounting best practices.

New FASB rules for nonprofit financial statements
Proper cash flow planning can also help avoid financial pitfalls and improve the organization’s overall financial stability. GAAP’s goal is to ensure companies’ financial statements are consistent across industries — allowing investors and the government to interpret them more easily. GAAP rules for nonprofits are intended to create transparency for donors and grant-makers. They also help the government monitor whether an organization should retain its tax-exempt status. Though the terminology differs, nonprofits and for-profits use the same accounting principles. During audits, nonprofit financial statements are examined to access if they are GAAP compliant.
- The main purpose of GAAP is to ensure that financial reporting is transparent and consistent from one organization to another.
- As an example, Zygmunt cited a donor who said a not-for-profit would receive a specific amount in his will.
- The Generally Accepted Accounting Principles—commonly known as GAAP—are a set of agreed-upon accounting standards that provide a framework for recording and reporting financial information.
- Firstly, it should include dedicated functions for capturing donations, grants, and membership fees, which require specific treatment compared to regular business revenue.
- Having robust internal policies and controls in place is essential for nonprofits to maintain financial integrity.
- Couch recommends keeping your staff and board members updated on what your accountants do and discover.
Use specialized software.
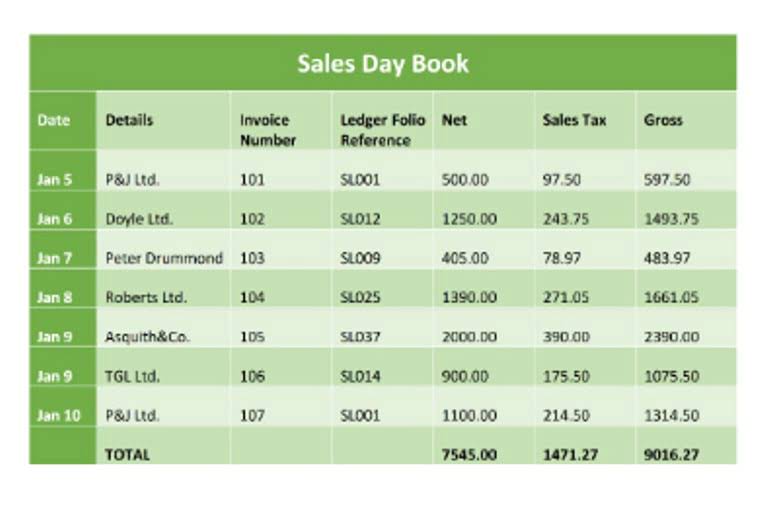
A tailored system not only ensures compliance with regulatory standards but also offers clarity and transparency regarding the use of donated funds. Non-profit organizations face unique challenges when it comes to accounting, chiefly because of the legal and regulatory stipulations that require them to maintain precise records of where their funds originate and how they are utilized. The main difference between for-profit and non-profit accounting lies in the objective of the organization. For-profit law firm chart of accounts firms aim to maximize profits, while non-profits focus on the organization’s mission.

Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
No matter how big or small nonprofits are, internal controls are essential for effective nonprofit accounting. However, this narrative is changing in the sector as more people become aware that overhead is a necessary expense for growth. Encourage your donors to judge your organization based on your impact in the community rather than how much you spend on fundraising and administrative expenses. Your nonprofit’s statement of cash flow shows how funding and cash moves in and out of the organization. It allows you to gauge how much is available to pay your expenses at any given time. Following best practices in financial reporting not only ensures compliance but also strengthens the organization’s operations and impact.